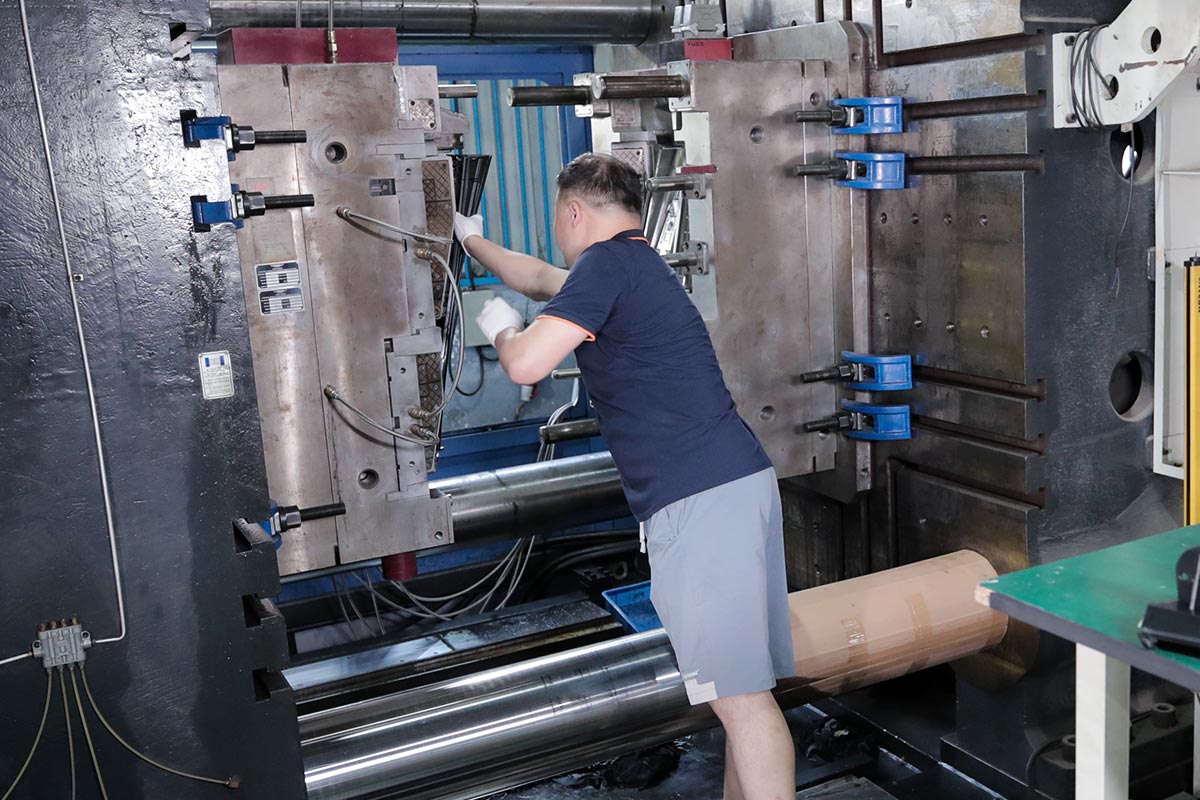
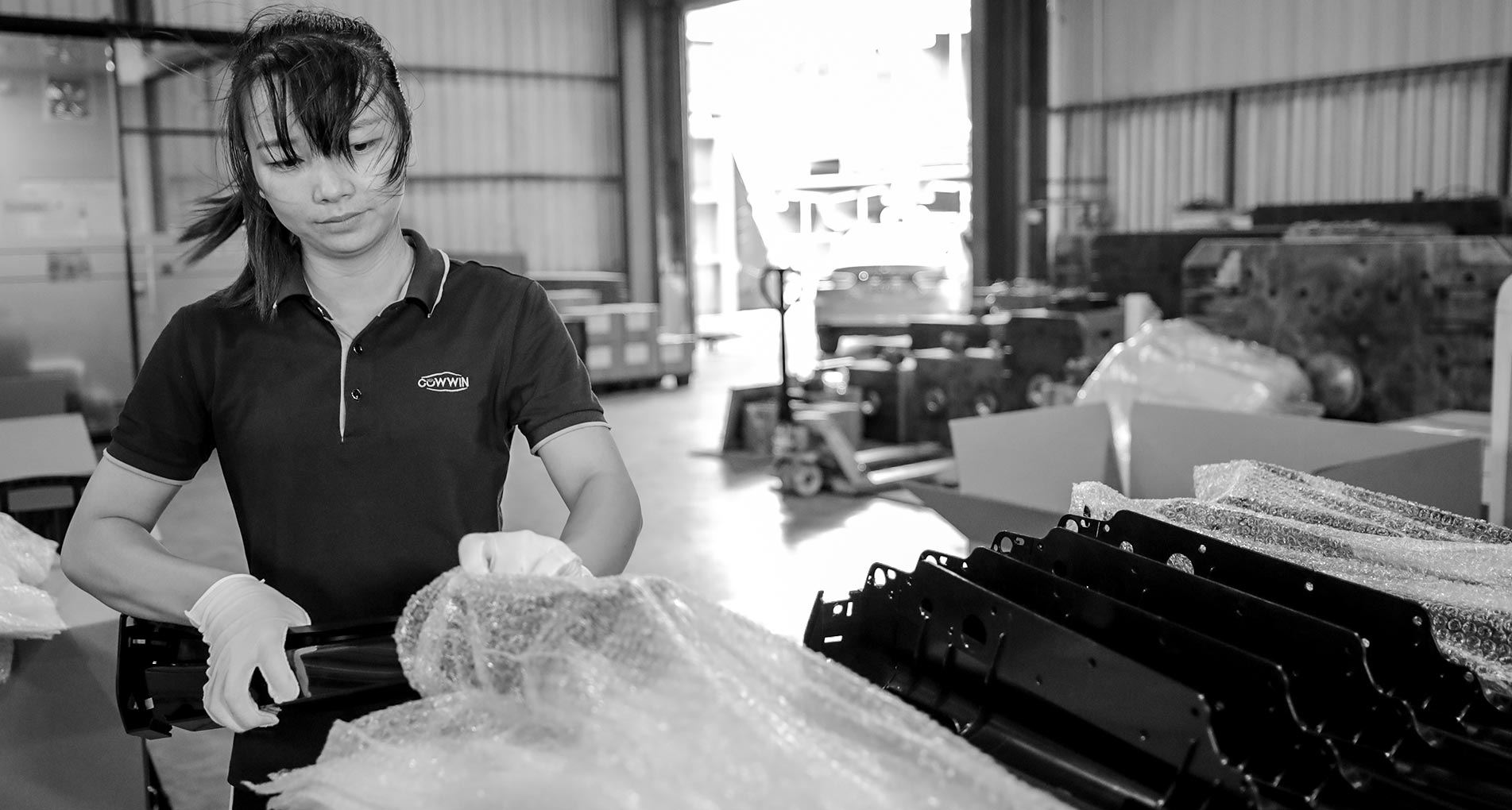
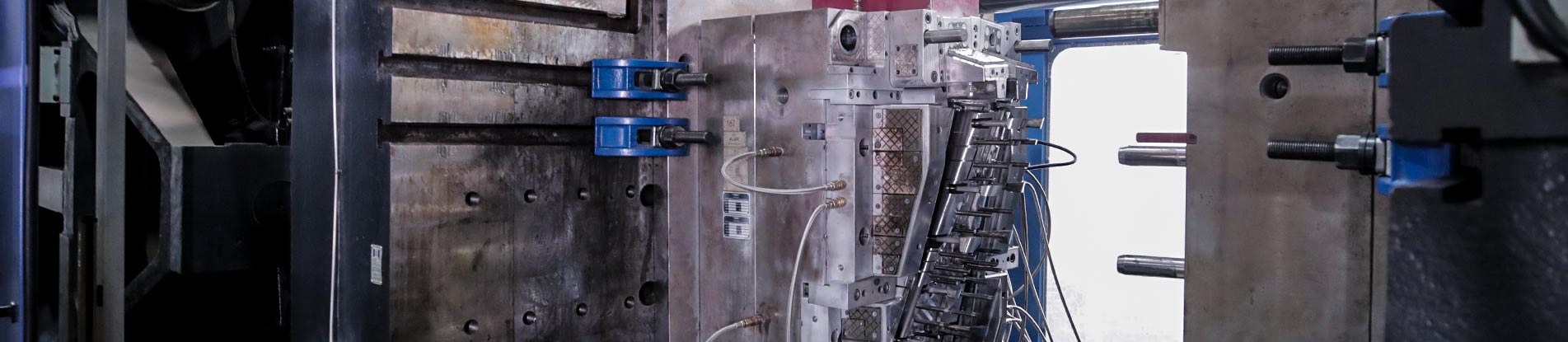
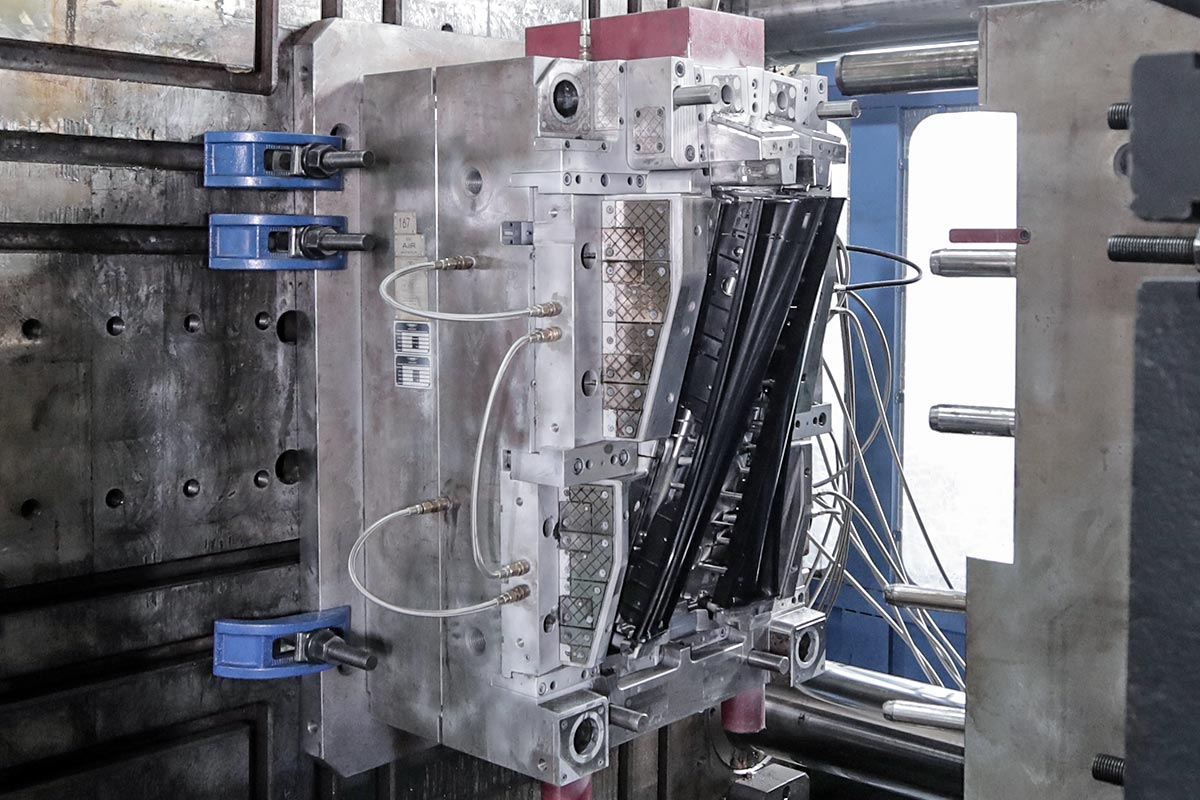
Injection Molding Processes
Make the move from prototyping to on-demand manufacturing for affordable, high-quality molded parts within days. This is when your prototyping tool is proof of concept once you shift to an on-demand manufacturing tool. Working with a single supplier that provides free design consultation services also massively speeds up the manufacturing process, allowing for greater supply chain flexibility, more consistent parts, and making qualification a breeze.
Consistency and Quality
We combine scientific (or decoupled) molding techniques, which optimize and lock in processing parameters to ensure part consistency—with extra attention paid to critical-to-quality dimensions using our proprietary automated CMM process.
Know Your Injection Molding Raw Materials
Virtually any type of thermoforming resin can be used in the injection molding process. There are thousands of different types of materials to choose from to enable you to achieve the performance, color, and quality that you need for your design. Check out our sheet of frequently used materials.